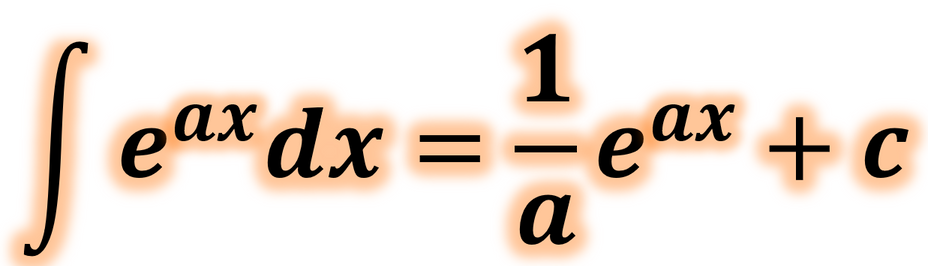integral of e to the ax

Pow
a > 0; ∫ eᵃˣ x = eᵃˣ/a + c.
what is the integral of e to the ax?
.
proof of the integral of e to the ax
We can prove why the integral of is equal to in several ways, some of which we will show below.
way 1
let .
(we take the differential of both sides of the equation)
.
way 2
let .
(we take the differential of both sides of the equation)
.
way 3
let .
(we take the differential of both sides of the equation)
.
way 4
by using the infinite series expansion of the function, we can prove that the integral of is equal to . The infinite series expansion of the function is as follows
(we take the integral of both sides of the equation)
(sides of the equation by a)
(a.c = 1)
Share Your Expertise, Earn Rewards!
Found this insightful? Imagine your knowledge generating income. Contribute your articles to bylge.com and connect with readers while unlocking your earning potential.